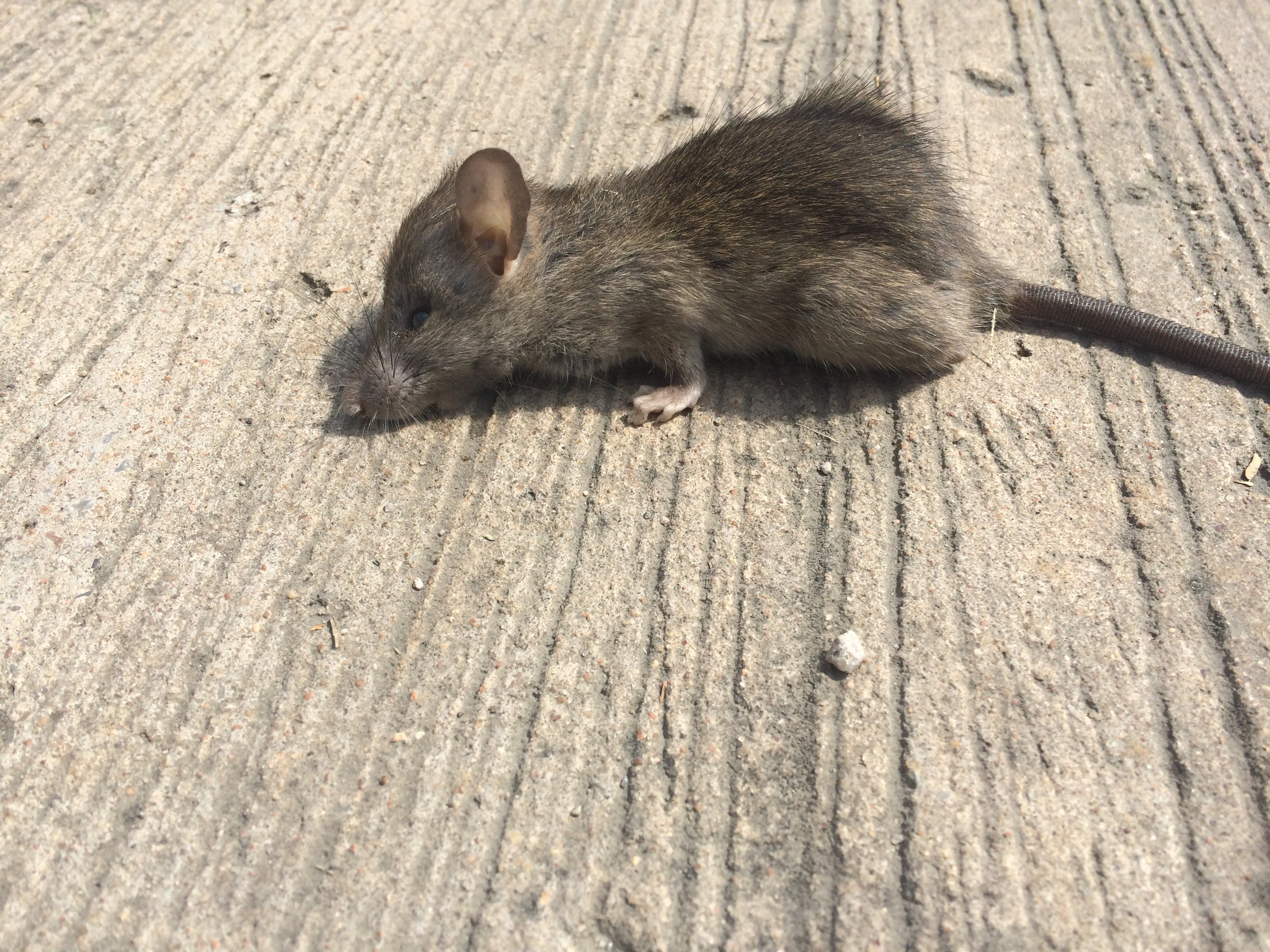
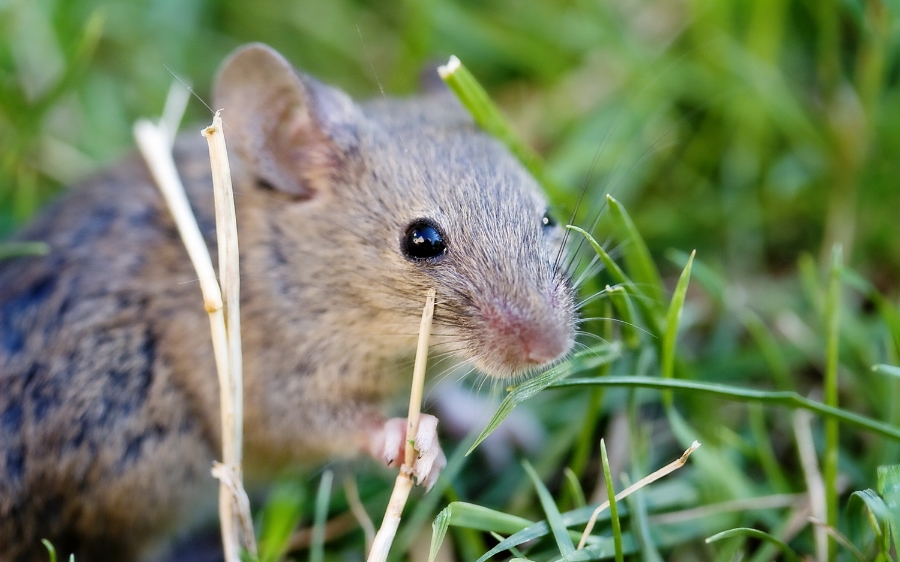
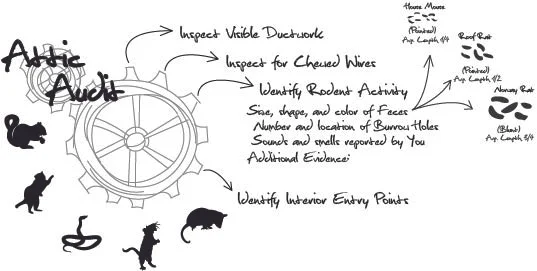
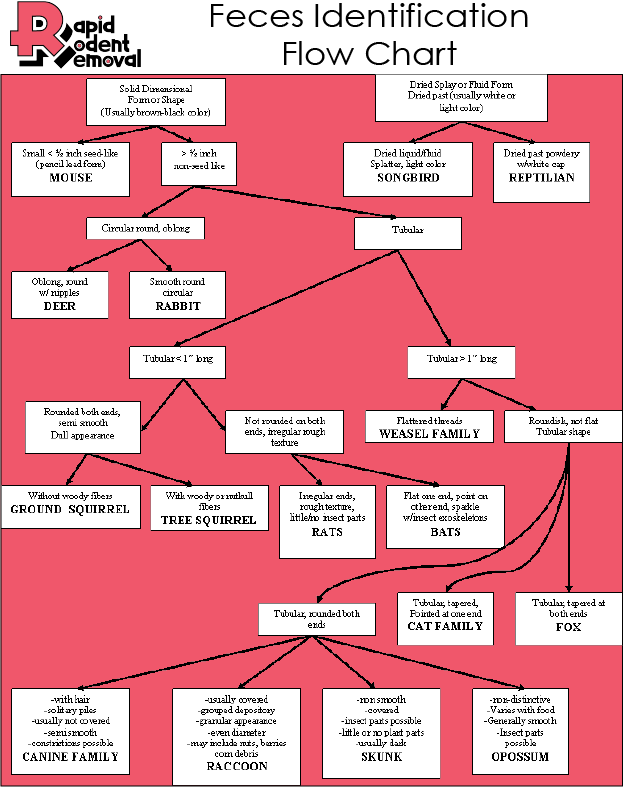
What does a mouse look like ?
Mice are small rodents, with a body length of about 3 to 4 inches and a tail that is about the same length. They have a thin, elongated body with a pointed snout, small rounded ears, and large black eyes. Their fur can be a variety of colors, including grey, brown, black, and white. Some species of mice have a light-colored belly and darker fur on their back. They have four legs and small feet with sharp claws, which they use for climbing and digging. They also have a long thin tail which is usually scaly and hairless.
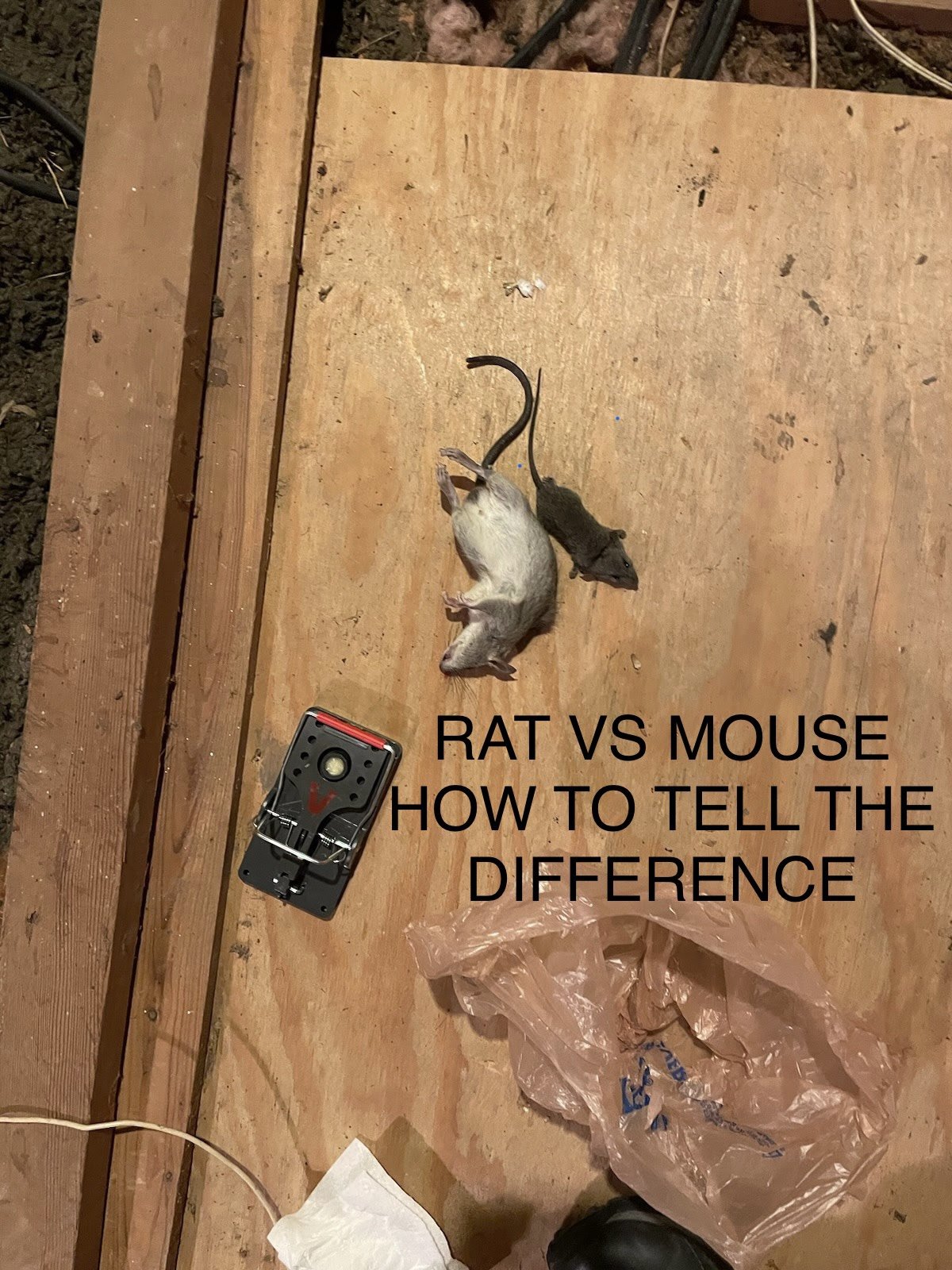
Mouse vs Rat : How to tell the difference
Mouse FAQ - All you need to know
The common House Mouse or Mice are small rodents that belong to the family Muridae. They have a small, slender body shape with a pointed snout, small ears, and a long, thin tail. They have soft fur that can be gray, brown, or black in color. They have large incisors that continuously grow and need to gnaw on hard objects to keep them filed down. They have small eyes and large ears which help them to navigate and locate food.
Common mouse behavior includes foraging for food, nesting, and avoiding predators. Mice are also known to be social animals and establish hierarchies within their colonies. They are active mostly at night and are known to be curious and exploratory. They are also known to be adept at problem-solving and have been known to navigate mazes and other obstacles to find food.
Mice have an excellent sense of smell, which they use to locate food, mates, and potential dangers. Mice have a highly developed olfactory system, with more than 1,000 different types of odor receptors in their noses, compared to the 5-6 types found in humans. This means they can detect a wide range of odors and can distinguish between different scents very easily.
Mice are also known for their intelligence and problem-solving abilities, which have made them a popular subject for research in fields such as neuroscience and behavioral biology.
Mice have a natural tendency to explore new environments, they can cover large areas and can find the way back to their home base with ease, even in mazes.
Normative Values for Mice
Lifespan 1-3 years
Adult weight : Males 20-30 g / Females 18-35g
Birth weight : 1-2 g - Heart rate 310-840 beats per minute
Respiratory rate 80-230 breaths per minute - Body temperature 36.5-38°C
The lifespan of a mouse can vary depending on the species and the conditions in which it lives. In the wild, mice typically live for around 6 to 12 months. However, mice kept in captivity as pets or lab animals can live for up to 2 years with proper care. The lifespan of a mouse also depends on factors such as diet, genetics, and exposure to disease or predators
The number of babies or "pups" that mice have can vary depending on the species and the conditions in which they live.
House mice (Mus musculus) can have litters of 3 to 14 pups, with an average of 6 to 8. They can have several litters per year, with females capable of reproducing when they are about 6 weeks old.
Field mice or wild mice (Apodemus sylvaticus) usually have smaller litters, usually 5-6 pups per litter and have one litter per year.
It's worth noting that the number of pups can also be affected by factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators.
mice are generally considered to be nocturnal animals, meaning they are most active at night. This behavior is thought to have evolved as a way for them to avoid predators and to take advantage of the cooler temperatures and lower levels of light during the night. However, some mice species are considered crepuscular, which means they are active during the twilight hours of dawn and dusk. This can vary depending on the species, the environment, and the availability of food.
Owls, Hawks, and other birds of prey: These birds hunt mice by using their sharp talons and beaks.
Snakes: Many species of snakes, such as the garter snake and the black rat snake, eat mice as a regular part of their diet.
Foxes, coyotes, and other mammals: These animals are known to hunt and eat mice, especially in areas where larger prey is scarce.
Domestic Cats: Cats are natural hunters, and they often catch and eat mice.
Additionally, some insects such as praying mantis are also known to eat mice.
It's worth noting that mice also fall prey to humans, as they are often considered pests and are trapped or poisoned to control their populations.
In some cultures and parts of the world, eating mice is not uncommon, especially in times of food scarcity, and it is considered a delicacy. However, in most developed countries, the idea of eating mice is considered unappetizing and it is not a common practice. Eating mice is also not considered safe due to the risk of disease transmission from the rodent to humans.
It's worth noting that in some cultures eating mice is considered taboo and is not allowed by the culture's customs or religion.
It's important to be aware of the laws and regulations in your area regarding the consumption of wild animals, as it may be illegal in some places.
In cultures where eating mice is traditional, it is usually prepared in a variety of ways, depending on the region and the preference of the people.
In some cultures, mice are roasted or grilled, and are often eaten as a delicacy.
In others, they are boiled or fried.
Some people also smoke or dry them to preserve them for later consumption.
It's worth noting that when mice are consumed as food, it is typically the adult mice that are used, and not the babies or "pups."
Mouse
Mice are social animals and tend to live in groups or colonies. They establish hierarchies within these colonies, with dominant individuals having priority over resources such as food and nesting sites. Mice are known to groom one another, huddle together for warmth, and even care for the young of other mice in the colony. These social behaviors are thought to have evolved as a way for mice to increase their chances of survival by sharing resources and information about potential dangers.
Mice are known to be highly adaptable animals and can be found in a wide range of environments, including urban, suburban, and rural areas. They are primarily nocturnal and are known to be highly active and curious animals. They are constantly exploring their environment and are able to fit through small openings and spaces. They are also known to be agile climbers and can climb walls, trees, and other structures with ease. They are active at night and spend most of their day hiding in burrows or other hiding places.
Mice are known to be highly social animals and live in large colonies or communities. They are territorial and establish dominance hierarchies within their colonies. They are known to be good at reproducing and females can give birth to litters of up to six young every three weeks.
Mice have a good sense of smell, taste, and touch, and use these senses to locate food. Their diet mainly consists of seeds, fruits, vegetables, and even insects and meat. They are also known to cache food for later use, burying it in the ground or hiding it in crevices.
Compared to rats, mice forage only short distances from their nest -- usually not more than 10-25 feet. When food and shelter are adequate, their foraging range may be only a few feet. For this reason, traps and other control devices must be placed in areas where mouse activity is most apparent. Mice prefer to travel adjacent to walls and other edges-- another critical point to remember when positioning control devices. Mice are very inquisitive and will investigate each new object placed in their foraging territory
Mice are omnivores and will eat a variety of foods, including seeds, fruits, vegetables, and insects. In the wild, they typically eat seeds, nuts, fruits, and insects. Domestic mice in captivity will eat a diet of commercial mouse food which is typically a combination of grains, seeds, fruits, and vegetables and also they are fed with small amounts of protein such as mealworms or crickets. They also require fresh water to drink.
Mice are opportunistic feeders, and their diet consists of a wide variety of food items, including seeds, fruits, vegetables, and even insects and meat. They can be a nuisance to homeowners because they can invade and contaminate food stores and also damage structures by gnawing on wood or electrical wiring, which can pose a fire hazard. They can also carry diseases such as hantavirus, salmonellosis and lymphocytic choriomeningitis.
What is a roof rat
How long do mice live
Mice can be a nuisance to homeowners because they can invade and contaminate food stores and also damage structures by gnawing on wood or electrical wiring, which can pose a fire hazard. They can also carry diseases such as hantavirus, salmonellosis and lymphocytic choriomeningitis.
Mice are known to be highly active and curious animals. They are constantly exploring their environment and are able to fit through small openings and spaces. Mice are also known to be agile climbers and can climb walls, trees, and other structures with ease. They are active at night and spend most of their day hiding in burrows or other hiding places.
articles:
What does a rat nest look like ?
What is a Squirrel King